In internet connectivity, bandwidth allocation refers to dividing the total bandwidth available on a network among various users, devices, or applications. This process ensures the smooth operation of the network by preventing any single user or application from consuming an excessive amount of bandwidth, thereby hindering the overall performance of others. Bandwidth allocation plays a crucial role in maintaining network stability and efficiency. Delve deeper into this concept by exploring Proxy Rotating’s comprehensive article on bandwidth allocation meaning.
Learn about what bandwidth allocation meaning
Bandwidth allocation is the process of assigning radio frequencies to different applications. Imagine a highway with only a finite number of lanes. Bandwidth allocation is like assigning those lanes to other types of vehicles (cars, trucks, motorcycles) to ensure smooth traffic flow. In the network world, bandwidth allocation ensures that no single user or application consumes excessive bandwidth, slowing down the internet for everyone else.
Bandwidth is a finite resource, just like the number of lanes on a highway. It’s measured in bits per second (bps) and determines how much data can be transferred over a connection at a given time. The higher the bandwidth, the faster the data transfer rate.
At its core, bandwidth allocation meaning encompasses managing data traffic across a network to prevent any individual user or application from dominating the connection. This management helps to avert network congestion and guarantees that all processes can access the resources they need for efficient operation.
Objectives behind allocating bandwidth
- Optimize network performance: By allocating bandwidth judiciously, networks can avoid bottlenecks and manage congestion, ensuring smooth operation and performance for all users and services. This is crucial in environments where network resources are limited compared to demand. Understanding the meaning of bandwidth allocation is essential for optimizing network performance.
- Ensure fair access: Bandwidth allocation helps ensure that all users or applications on a network have fair access to resources. It prevents any single user or service from monopolizing the bandwidth, guaranteeing a balanced distribution that benefits everyone.
- Support critical applications: Some applications, like VoIP, video conferencing, or online gaming, require a specific minimum bandwidth to function effectively. Bandwidth allocation allows network administrators to prioritize these critical applications, ensuring they have the necessary resources for optimal performance.
- Manage network traffic: Through strategic bandwidth distribution, administrators can control and manage network traffic more effectively, preventing congestion and ensuring that high-priority data flows smoothly.
- Enhance user experience: By minimizing network congestion and ensuring that essential applications receive the bandwidth they need, the concept of bandwidth allocation meaning plays a direct role in enhancing the overall user experience. This includes reducing buffering times for streaming media, improving call quality in VoIP applications, and ensuring faster response times for web applications.
- Cost efficiency: Effective bandwidth allocation can also be a cost-saving measure for service providers and businesses. Maximizing the efficiency of existing network infrastructure, informed by a deep understanding of bandwidth allocation, can delay or eliminate the need for costly upgrades.

The role and importance of bandwidth allocation
Now that we’ve grasped the concept of bandwidth allocation. Let’s explore why ensuring a smooth-running and efficient network is vital.
Ensure effective network use
Effective bandwidth allocation is instrumental in ensuring that a network’s resources are utilized as efficiently as possible. It facilitates a systematic approach to distributing available bandwidth among various applications and users, preventing any single entity from consuming more than its fair share. This astute bandwidth management is crucial for optimizing network performance, ensuring that all tasks have access to the resources they need to operate smoothly without causing unnecessary strain on the network infrastructure.
Improve service quality
The quality of network services is directly influenced by how well bandwidth is allocated. By prioritizing critical services and managing bandwidth allocation dynamically, networks can maintain high performance even under heavy load, significantly reducing latency and packet loss. This leads to a noticeable improvement in real-time applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and VoIP services, directly impacting user satisfaction and perceived service quality.
Meet diverse user needs
In today’s digital age, users have a wide range of needs and expectations from their network connections, from basic web browsing to high-definition video streaming and sophisticated cloud-based applications. Effective bandwidth allocation ensures that these diverse requirements are met by appropriately distributing network resources. This adaptability is crucial for catering to the varying demands of different users, ensuring that everyone, from casual internet users to heavy data consumers, receives a consistent and satisfactory online experience.
Minimize network congestion
Bandwidth allocation is pivotal in minimizing network congestion, a common challenge for many networks. By controlling bandwidth distribution and prioritizing essential traffic, networks can prevent bottlenecks and efficiently manage traffic flows. This is especially important in peak usage times or situations where the network faces an unexpected surge in demand. Effective congestion management ensures that the network remains stable and responsive, avoiding the slowdowns and disruptions that can occur when resources are stretched too thin.

Popular bandwidth allocation methods
Now, let’s explore the various methods for managing and distributing bandwidth effectively within a network. These methods, like fixed or dynamic allocation, each have strengths and weaknesses, making it crucial to choose the right one for your needs.
Fixed bandwidth allocation
Fixed Bandwidth Allocation involves assigning a predetermined bandwidth to each user or device, regardless of their current demand or requirements. This method is straightforward but needs more flexibility as it adapts to dynamic changes in network traffic or individual user needs.
Dynamic bandwidth allocation
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation is a technique that allows bandwidth distribution to be adjusted on demand among different users. It is more efficient than fixed allocation as it can adapt to instantaneous traffic demands, ensuring fair access to network resources and improving overall performance.
On-demand bandwidth allocation
On-demand bandwidth Allocation refers to a network’s capability to adjust bandwidth dynamically based on real-time data transmission needs. It provides flexibility and efficient utilization of network resources by scaling bandwidth up or down according to varying user demands and application requirements.
QoS-based Bandwidth allocation
QoS-based Bandwidth Allocation prioritizes network traffic by allocating bandwidth based on the quality of service requirements of different applications. This method ensures critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth, improving the network’s ability to handle mission-critical operations and maintain service quality. Critical applications like video calls receive higher priority compared to regular web browsing.

Advantages and disadvantages of bandwidth allocation methods
| Fixed Bandwidth Allocation | Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation | On-Demand Bandwidth Allocation | QoS-based Bandwidth Allocation | |
| Advantages | Simplicity in implementation and cost-effectiveness due to less computational requirements. | Efficient use of available bandwidth reduces call blocking and improves call quality by adjusting to traffic volume. | Offers flexibility and cost-efficiency by scaling bandwidth according to real-time needs, preventing underuse and overload. | Prioritizes critical applications, ensuring they receive the necessary bandwidth for optimal performance, which enhances user experience. |
| Disadvantages | Lack of flexibility, as it cannot adapt to changing traffic demands, leading to potential underutilization or congestion. | If resources are not appropriately managed, higher complexity in equipment and algorithms may result in increased operational costs and potential call drops. | It may require more sophisticated network management tools and introduce latency during allocation. | It can be complex to configure and may require ongoing adjustments to maintain the desired level of service quality. |
Choosing the method
The selection of a bandwidth allocation method depends mainly on your network’s specific needs and characteristics, including user demands, application requirements, and traffic variability.
- For simple networks with predictable usage, Fixed Allocation might suffice.
- For dynamic environments with fluctuating user demands, Dynamic Allocation is a good choice.
- If users have temporary high-bandwidth needs, consider On-Demand Allocation.
- For networks where prioritizing critical applications is crucial, QoS-based Allocation is ideal.
Application of bandwidth allocation in practice
- Home Wi-Fi: Your home router uses a combination of allocation methods. It might reserve a fixed amount for critical devices like your work laptop while dynamically allocating the rest based on which devices are streaming, gaming, or browsing online.
- Corporate networks: In an office, bandwidth allocation prioritizes critical business applications like video conferencing or file servers. This ensures smooth operation for essential tasks while allowing employees to browse the web or use work chat tools.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): When you stream a movie or download a large file, CDNs use bandwidth allocation to distribute the content efficiently. They allocate more bandwidth to high-demand areas, ensuring a smooth streaming experience for everyone.
- Cellular networks: Mobile providers allocate bandwidth to manage traffic between cell towers and user devices. This ensures calls don’t drop during peak usage and data transfers happen at optimal speeds.
- Online gaming: Online games require consistent bandwidth for smooth gameplay. Gaming platforms might use a combination of fixed and dynamic allocation to prioritize gaming traffic and avoid lag.
- Streaming services: Streaming platforms use bandwidth allocation to manage content delivery, ensuring that all users receive a consistent quality of service. By dynamically allocating bandwidth based on current demand and network conditions, these services can minimize buffering and provide a smooth streaming experience.
- Cloud Computing: Providers allocate bandwidth to support the efficient transfer of data and ensure that high-priority tasks, such as real-time data analytics or critical backups, have the necessary resources to proceed without interruption.
- IoT Devices: With the proliferation of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, bandwidth allocation becomes crucial to ensure that all devices, from smart thermostats to security cameras, can communicate effectively without overwhelming the network. This ensures that critical alerts and data are transmitted promptly while maintaining network health.
Answer questions about bandwidth allocation meaning
Can bandwidth allocation affect internet speed?
Yes, bandwidth allocation can affect the internet speed users experience. Controlling how bandwidth is distributed can ensure that no single user or application hogs all the bandwidth, thereby improving the speed and quality of service for others.
How do ISPs use bandwidth allocation?
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) use bandwidth allocation to manage network traffic, ensuring all subscribers receive fair and consistent service. They may also use it to offer different service tiers with varying bandwidth limits to accommodate user needs and price points.
How can bandwidth allocation support Quality of Service (QoS)?
Bandwidth allocation supports QoS by ensuring critical applications and services receive the bandwidth they need to function effectively. It allows network administrators to prioritize traffic, guaranteeing performance levels for high-priority tasks.
Is it possible to override bandwidth allocation settings?
In some networks, mainly corporate or managed environments, administrators can adjust or override bandwidth allocation settings to respond to changing needs or to address specific issues. However, this capability depends on the network’s management policies and the flexibility of its infrastructure.
How can I find out how bandwidth is allocated on my network?
You should consult your network administrator or ISP to understand how bandwidth is allocated. They can provide details on the specific allocation methods and policies in use. For home networks, some routers offer interfaces that show how bandwidth is being used and allow for basic allocation settings.
Tool to support effective bandwidth allocation
Essential network tools (suited for home or small networks):
- Router configuration: Most routers offer built-in features for basic bandwidth allocation. You can often set priority devices or limit bandwidth for specific devices. (Web Interface or Mobile App)
Network monitoring and management tools:
- Open-source tools: Free and open-source software like pfSense or OpenWrt offer advanced configuration options for bandwidth allocation, including traffic shaping and QoS (Quality of Service) prioritization. (Requires technical knowledge)
- Commercial network management software: Paid solutions from Cisco Meraki, Netgear Insight, or Ubiquiti offer user-friendly interfaces for bandwidth monitoring, allocation, and traffic shaping. These tools often come with additional features like network security and device management. (Subscription fees may apply)
Advanced tools for enterprise networks:
- Network Traffic Analyzers (NTA): These tools provide deep insights into network traffic patterns, allowing you to identify bandwidth hogs and optimize allocation strategies. Tools like SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor or ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer offer comprehensive traffic analysis and bandwidth management capabilities.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) Solutions: SDN allows more programmatic control over network traffic routing and bandwidth allocation. While complex to set up, SDN provides highly granular control and automation for large, dynamic networks.
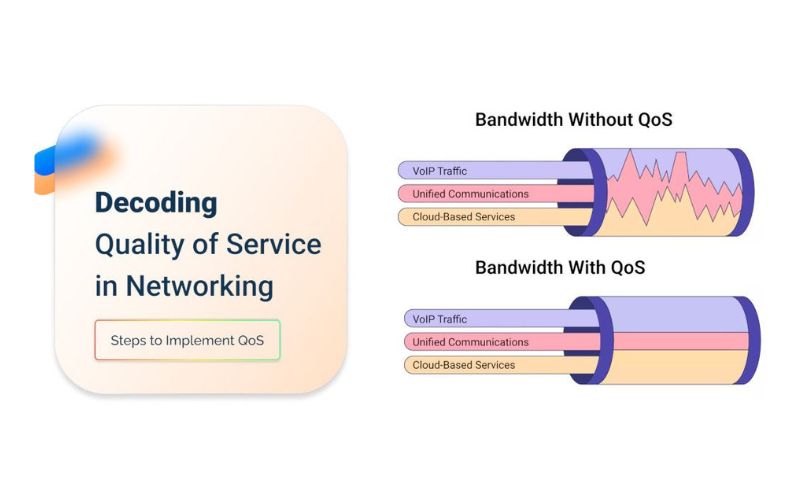
In conclusion, understanding bandwidth allocation meaning is essential for optimizing network performance and ensuring fair access to resources across various users and applications. This concept plays a pivotal role in managing network efficiency, preventing congestion, and supporting the quality of service for critical operations. By effectively distributing network bandwidth, administrators can cater to diverse user needs and maintain optimal service levels. For those seeking to deepen their knowledge on this topic and explore further insights into the intricacies of bandwidth allocation, visit our website, Proxy Rotating, to be offered a wealth of information and resources tailored to enhance your understanding and application of bandwidth allocation strategies.
>>> See more:
Bandwidth definition in electronics
Bandwidth needed for streaming
