Monitoring network bandwidth is crucial in efficient network management as it provides essential information to ensure the network infrastructure is used optimally and effectively. With such significant benefits, more and more bandwidth monitoring tools are being developed. So, what benefits do bandwidth monitoring tools offer? What are the popular bandwidth monitoring tools, or how do you choose the right Bandwidth monitoring tools? The following article will address these topics.
What is a bandwidth monitor tool?
A bandwidth monitor tool is a software application or hardware device designed to measure and track the bandwidth usage on a computer network. In this context, bandwidth refers to the rate at which data is transferred across a network connection, usually measured in bits per second (bps). These tools help network administrators, IT professionals, and individual users understand how their network’s bandwidth is consumed by monitoring data flow to and from the internet and within the network.

Key features of Bandwidth monitoring tools
Bandwidth monitoring tools typically include a range of key features that assist in managing and analyzing network bandwidth usage. Here are some standard features often found:
- Data collection: Bandwidth monitoring tools collect network traffic data from network devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls. This data is then stored for analysis and reporting.
- Data analysis: These tools analyze network traffic data to identify trends and patterns in bandwidth usage. They identify which applications and services are using network bandwidth, helping users understand more about the sources of bandwidth consumption.
- Reporting: Provide instant views of bandwidth usage in real-time, enabling users to quickly identify and address bandwidth-related issues.
- Alerts: Bandwidth monitoring tools automatically notify users via email or SMS when bandwidth usage exceeds predetermined thresholds, helping to prevent excessive usage.
Why are Bandwidth monitoring tools important?
Bandwidth monitoring tools play a crucial role in managing and maintaining the health and efficiency of a network. These tools are essential for several key reasons:
- Performance optimization
Bandwidth monitoring helps identify how the network bandwidth is used and by which applications or users. This information is critical for optimizing network performance, ensuring that bandwidth is available for critical applications and services, and preventing congestion and bottlenecks.
- Cost management
Monitoring tools can help businesses with limited bandwidth capacities or those that incur costs based on bandwidth usage manage costs effectively. Organizations can make informed decisions about bandwidth allocation by understanding usage patterns, potentially reducing the need for costly bandwidth upgrades.
- Security
Bandwidth monitoring can enhance security by identifying unusual or suspicious activity, such as spikes in traffic that could indicate a security breach, such as a DDoS attack or a network intrusion. Early detection of such anomalies allows for timely intervention to mitigate security risks.
- Troubleshooting
Network problems can often lead to decreased productivity. Bandwidth monitoring tools can help quickly identify and resolve network issues, such as failed network devices or improper configurations, by pinpointing the source of a problem.
- Capacity planning
Monitoring tools provide historical data on bandwidth usage trends, which is invaluable for future network planning and capacity decisions. This data helps predict growth and scalability needs, ensuring that the network can efficiently handle expected increases in traffic without performance degradation.
- Compliance and accountability
In environments where regulatory compliance requires specific data traffic handling, bandwidth monitoring can help ensure compliance by providing logs and records of data transmission activities. It also supports accountability by tracking how departments or individuals utilize network resources.
- Quality of service (QoS)
Effective bandwidth monitoring allows administrators to enforce QoS policies by prioritizing bandwidth for critical applications over less important traffic. This ensures crucial applications perform optimally even when the network is heavy.
- Enhanced user experience
For service providers, particularly ISPs and hosting services, bandwidth monitoring is critical to delivering a consistent and reliable user experience. Providers can maintain high customer satisfaction by ensuring sufficient bandwidth and quickly addressing quality issues.
In summary, bandwidth monitoring tools are vital for maintaining an efficient, secure, and cost-effective network. They provide essential insights that help proactively manage network resources, improving the performance and reliability of IT infrastructures.

How do you check network bandwidth usage?
Checking network bandwidth usage involves monitoring the amount of data transmitted and received across a network within a given time frame. This can help identify bottlenecks, understand performance issues, and ensure the network is not overloaded. Here are some standard methods and tools you can use to check network bandwidth usage:
Router’s Built-In software
Many modern routers have built-in tools that allow you to monitor internet usage directly from the router’s admin panel. This is accessible through a web interface, which you can access by entering the router’s IP address in a browser. The interface typically provides information about which devices are connected and how much data they use.
Network monitoring software
There are various software tools available that can provide detailed insights into network bandwidth usage. Here are a few examples:
- Wireshark is a network protocol analyzer that can capture and display data traveling back and forth on a network in real-time. It’s handy for deep technical analysis and troubleshooting.
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor: This comprehensive network performance monitoring tool can automatically detect network devices and performance issues, display performance metrics in real-time, and provide detailed reporting.
- PRTG Network Monitor: Offers a full suite of monitoring tools, including bandwidth usage, with customizable dashboards and easy-to-read visualizations.
Command line tools
- Windows: You can use the netstat command in the Command Prompt to see the active connections and their performance. For more detailed usage stats, Performance Monitor (perfmon) is a built-in Windows tool that tracks network performance.
- Linux: Tools like if top or unload display real-time bandwidth usage interface-by-interface.
- MacOS: You can use the built-in Activity Monitor, which includes a network usage section showing data sent and received for active connections.
Third-party applications
- NetBalancer, NetGuard, and GlassWire are third-party applications for Windows that allow you to monitor internet traffic and check which applications are using your bandwidth.
- Little Snitch for macOS provides a similar service, focusing more on outbound connections and offering detailed network traffic controls and alerts.
ISP Tools
Some Internet Service Providers (ISPs) offer tools through their customer portals that allow you to monitor your total internet usage, which can be helpful if you have a data cap.
Smartphone apps
- Android and iOS devices often have built-in settings that track data usage per application, accessible via the device’s settings menu.
- Apps like My Data Manager can also help monitor mobile data usage and provide alerts when you are close to reaching a data limit.
These tools and methods can give you a comprehensive view of how bandwidth is utilized within your network, helping you manage resources more effectively and troubleshoot any issues.

How do you minimize the consumption of bandwidth?
Minimizing bandwidth consumption can improve network performance, reduce costs, and stay within data usage limits. Here are several strategies and tips for effectively reducing bandwidth consumption:
- Limit non-essential traffic
Implement usage policies: Establish guidelines that limit recreational or non-business-related internet use during work hours.
Content filters: Use web filtering tools to block access to high-bandwidth sites, such as video streaming services, social media platforms, and online gaming sites.
- Optimize web usage
Data compression: Use compression tools or services that minimize the size of the data being sent over the network. Many web servers and browsers support automatic data compression.
Caching: Implement caching mechanisms to store local copies of frequently accessed web resources, reducing the need to fetch them repeatedly from the internet.
- Network traffic management
Quality of service (QoS): Configure QoS on network routers and switches to prioritize critical business applications and restrict bandwidth for less critical services.
Bandwidth throttling: Set bandwidth limits for specific applications, users, or devices to prevent any single user or application from consuming too much bandwidth.
- Upgrade and optimize hardware and software
Efficient hardware: Use modern networking hardware to handle high data loads more effectively.
Update and maintain: Ensure that all networked systems are regularly updated to eliminate bugs that may cause excessive bandwidth usage. This includes firmware updates on network hardware.
- Monitor and audit usage regularly
Network monitoring tools: Utilize network monitoring tools to monitor bandwidth usage patterns and identify potential issues or abusers.
Regular audits: Review network usage reports regularly to understand how bandwidth is used and adjust policies or configurations as needed.
- Use local servers for frequent access
Local hosting: For businesses, hosting commonly used resources on local servers can reduce dependence on external bandwidth as data is transmitted over the local network.
Distributed network architecture: Consider a distributed approach where resources are placed closer to the users (e.g., branch offices) to minimize long-haul bandwidth usage.
- Optimize email settings
Email management: Encourage or enforce policies to reduce the size of email attachments, or use cloud links instead of attachments. Employ email filtering to reduce spam, which can also consume bandwidth.
- Streamline video and audio usage
Compression: Use video and audio compression technologies to reduce the file size without significantly affecting quality.
Lower quality settings: For non-critical uses of video and audio streaming, lower the quality settings to decrease the amount of data transmitted.
- Remote desktop settings
Optimize settings: If using remote desktop solutions, optimize their settings to consume less bandwidth, such as reducing screen resolution and disabling desktop background.
Implementing these strategies can help significantly reduce bandwidth usage, enhance network performance, and ensure a more efficient use of resources. Each organization may require a different combination of these techniques based on their specific needs and the nature of their network traffic.
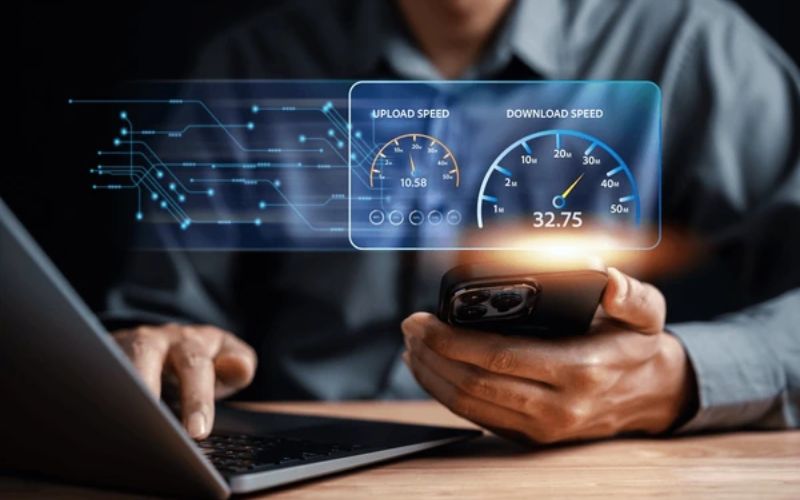

Popular Bandwidth monitoring tools
Many favored bandwidth monitoring tools are commonly used for monitoring, analyzing, and managing network bandwidth usage. Some of the well-known tools include:
- Wireshark: As one of the leading free and open-source network packet analyzers, Wireshark provides deep insights into network traffic, helping to identify issues and analyze bandwidth usage.
- SolarWinds Network Bandwidth Analyzer Pack: This commercial solution offers comprehensive bandwidth analysis and network performance monitoring, including custom alerts and reports.
- PRTG Network Monitor: PRTG offers comprehensive network monitoring with the ability to monitor bandwidth, performance, and other network issues. It also includes user-friendly dashboards and real-time alerts.
- NetFlow Analyzer: As an in-depth network traffic analysis solution, NetFlow Analyzer focuses on analyzing NetFlow, sFlow, cFlow, J-Flow, and other protocols, helping to optimize bandwidth usage and detect unusual traffic patterns.
- Nagios: Nagios provides extensive network monitoring, including bandwidth monitoring, with flexible alerting capabilities and detailed reporting.
- BandwidthD: An open-source bandwidth monitoring tool, BandwidthD tracks network traffic and generates HTML graphs reflecting bandwidth usage over time.
- Ntopng: The next generation of top ntopng is an open-source network traffic analysis tool that offers detailed insights into network traffic in real time.
- Zabbix: Zabbix is a comprehensive open-source network monitoring solution that can monitor bandwidth, network performance, and more.
- Cacti: Cacti offers network monitoring through RRDTool graphs, with the ability to monitor bandwidth and generate easy-to-understand charts.
Each tool has unique features and is designed to meet the specific needs of users or organizations.

How to choose the right Bandwidth monitoring tool
Choosing the right bandwidth monitoring tool requires considering several factors based on your network environment, business needs, and budget. Here are some steps and essential aspects to consider when selecting a tool:
Identify goals and needs
- Monitoring Scope: Determine whether you need to monitor the entire network, only a part of the network, or specific applications.
- Monitoring Objectives: Understand clearly the goals of bandwidth monitoring, such as improving performance, detecting issues, or optimizing costs.
Evaluate necessary features
- Real-time and Historical: Determine whether you need real-time monitoring, historical usage tracking, or both.
- Reporting and Alerts: Look for the ability to customize reports and alerts based on specific thresholds.
- Traffic Analysis and Bandwidth Shaping: Is there a need for detailed network traffic analysis and bandwidth shaping?
- Integration with Other Systems: Should the tool easily integrate with other network management, security, or IT systems?
Consider scalability: The tool must be scalable to accommodate network growth and future bandwidth usage needs.
Assess complexity and usability: Consider the balance between features and the user interface. There may be better choices than a powerful but difficult-to-use tool.
Compatibility and support: Ensure the tool is compatible with your current network infrastructure and is fully supported by the vendor.
Consider cost: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), including price, maintenance, and upgrades. Compare the available budget with the cost of the tool.
Test and evaluate: Take advantage of free trials or demos (if available) to test the tool in your actual environment.

A bandwidth monitoring tool is a crucial instrument that helps organizations manage their networks effectively. Choosing the right tool can assist organizations in resolving network performance issues, enhancing network security, and planning for future bandwidth needs. This article by Proxy Rotating has given you a better understanding of bandwidth monitoring tools.
>> See more:
Bandwidth needed for streaming
Bandwidth and frequency relationship
