In the world of electronics, bandwidth reigns supreme. It defines the range of frequencies a device can handle, acting like a highway for information. Imagine a radio station – its bandwidth determines the amount of data it can transmit, shaping the audio quality. However, bandwidth is affected by several factors. This article, Proxy Roating will delve deeper into the concept of bandwidth, exploring the secrets behind the smooth flow of information in your electronic devices. Let’s explore together!
What is bandwidth?
Definition of bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the maximum capacity of a wired or wireless communications link to deliver data via a network connection in a given amount of time. It is not a measure of network speed; rather, it represents the maximum throughput—the amount of data transferred per second. Think of bandwidth as the volume of water that can flow through a conduit: the wider the pipe (higher bandwidth), the more data it can handle simultaneously.
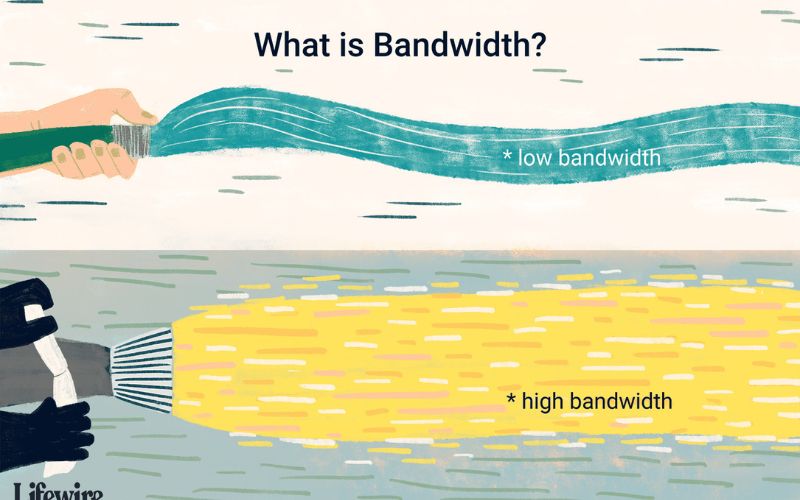
The unit of bandwidth
The unit of measurement for bandwidth is Hertz (Hz), which quantifies the frequency range over which a system can operate or transmit information. One Hertz represents one cycle per second. Bandwidth values are often expressed in terms of kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), or even gigahertz (GHz), indicating thousands, millions, and billions of cycles per second, respectively. This metric allows for the comparison and evaluation of the data-carrying capacity of different systems and technologies.
Bandwidth is often associated with frequency. In analog signals, it represents the difference between the highest and lowest frequencies within a given range.
For instance, if a telephone line can carry frequencies from 300 Hz to 3300 Hz, its bandwidth is 3300 – 300 = 3000 Hz (or 3 kHz)
Bandwidth vs. transmission speed
While both terms deal with data transfer, they represent different aspects. Bandwidth defines the capacity of a channel, like the number of lanes on a highway. Transmission speed, on the other hand, refers to the actual rate at which data travels through that channel, similar to the speed of the vehicles on the highway.
Bandwidth refers to the capacity of a link to handle data, while transmission speed (also called throughput) represents the actual rate at which data flows. A higher bandwidth connection allows for faster transmission speeds, but they are not synonymous.
Roles of bandwidth in electronics
Bandwidth plays a crucial role in electronics, acting as a fundamental parameter that shapes the design, functionality, and performance of a wide array of electronic devices and communication systems.
Facilitates high-speed data transmission
In the electronics industry, bandwidth directly influences the rate at which data can be transmitted over a network. Higher bandwidth allows for more data to be transferred simultaneously, enabling high-speed internet connections, faster download rates, and smoother streaming services.

Determines system capacity
The bandwidth of a system determines its capacity to handle data. In telecommunications, for instance, bandwidth is key to supporting the number of concurrent calls or data transfer activities a system can manage without degradation in quality.
Enhances signal quality
In audio and video electronics, bandwidth is essential for maintaining high-quality signals. A wider bandwidth means that a greater range of frequencies can be transmitted, which is crucial for high-definition audio and video outputs.
Enables advanced applications
The role of bandwidth extends to enabling advanced applications and services, such as cloud computing, virtual reality (VR), and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies require substantial bandwidth to function effectively, influencing the design and development of related electronic products.
Basic bandwidth calculation formula
– Define the range of frequencies a system can accommodate
The formula is: Bandwidth = f_max – f_min
Example: Imagine a radio transmitter designed to broadcast on the FM radio band. The FM radio band typically ranges from 88 MHz (f_min) to 108 MHz (f_max). Using the formula:
Bandwidth = 108 MHz (f_max) – 88 MHz (f_min) = 20 MHz
Therefore, this radio transmitter can accommodate a range of frequencies of 20 MHz, allowing it to broadcast on various FM radio stations within that band
– Determine how much bandwidth is needed for a specific application or website
The formula is: Bandwidth (bps) = Number of users × Average data transfer rate (bps) × Usage factor
Example: Suppose you’re running a video conferencing application for a small business with 20 employees (number of users). The average data transfer rate for a video call is estimated to be around 1 Mbps (average data transfer rate). You anticipate an average usage factor of 70% (usage factor), meaning not all users will be in video calls simultaneously.
Bandwidth (bps) = 20 users × 1 Mbps/user × 0.7 = 14 Mbps
Considering the usage factor, this calculation suggests that a minimum bandwidth of 14 Mbps would be sufficient to handle video conferencing for most of your employees at a time.
– Estimate the bandwidth for a new site
The formula is: Bandwidth (GB) = Average page size (MB) × Average number of visitors × Average number of pages per visitor × 30 days.
Example: Let’s say you’re creating a new website with an average page size of 2 MB (average page size). You expect an average of 1000 visitors per day (average number of visitors) browsing 3 pages each on average (average number of pages per visitor).
Bandwidth (GB) = 2 MB/page × 1000 visitors/day × 3 pages/visitor × 30 days = 180,000 MB
Since there are 1024 MB in 1 GB, this translates to:
Bandwidth (GB) = 180,000 MB / 1024 MB/GB ≈ 176.76 GB
This estimation indicates that your website might require roughly 176.76 GB of bandwidth per month to accommodate the expected visitor traffic and browsing behavior.
Factors influencing bandwidth in electronics
Connection cable type
The type of connection cable significantly impacts bandwidth. Wired cables, such as Ethernet, offer high data rates due to their dedicated channels and shielding against interference. In contrast, wireless connections, like Wi-Fi, may experience signal degradation over distance or due to obstacles. Furthermore, copper cables have limitations compared to fiber optic cables. Thicker copper cables generally offer better bandwidth compared to thinner ones.
Processing capacity of the device
The processing power of a device affects its ability to handle data. Faster processors can manage higher data rates, while slower ones may bottleneck data flow. For instance, a powerful router can handle multiple simultaneous connections without compromising bandwidth.

Transmission signal type
Different signal types impact bandwidth. Analog signals, like those in older telephone lines, have limited bandwidth. In contrast, digital signals, such as those in fiber-optic cables, offer much higher data rates. The modulation technique (e.g., AM, FM, QAM) also influences bandwidth. The type of signal being transmitted can also affect bandwidth.
Disturbance in the environment
Interference from external sources like electromagnetic waves or physical obstacles (walls, buildings)can disrupt data transmission and reduce effective bandwidth. This is why maintaining a clear line of sight for wireless connections or using shielded cables can be important for optimal bandwidth performance.

Tips to improve network bandwidth
Use high-quality network cables
Invest in good-quality Ethernet cables. Cat 6 or Cat 7 cables offer better performance and less interference compared to older versions. Properly shielded cables minimize signal loss and ensure reliable data transmission.

Upgrade network equipment
Outdated routers and modems can bottleneck your network. Consider upgrading to newer models that support faster speeds, better coverage, and advanced features like dual-band Wi-Fi or MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output).
Minimize devices using the same bandwidth
Too many devices sharing the same bandwidth can slow down your network. Prioritize critical devices (such as workstations or streaming devices) and limit non-essential ones. Use Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router to allocate bandwidth effectively.

Contact network service provider to upgrade package
Reach out to your internet service provider (ISP). Inquire about higher-speed plans or any promotional offers. Upgrading your package can significantly boost your available bandwidth, especially if you’re experiencing slow speeds or frequent buffering.

Bandwidth FAQs
1. The greater the bandwidth, the faster the network speed, right?
Mostly true. Bandwidth is like the number of lanes on a highway. Higher bandwidth allows more data to flow simultaneously, potentially leading to faster speeds. However, other factors like network congestion and your ISP’s infrastructure can also affect speed.
2. How to check internet bandwidth?
Online tools: Many internet service providers (ISPs) offer online tools to check your bandwidth.
Speed test websites: Use websites like https://www.speedtest.net/ to measure your download and upload speeds (which are related to bandwidth).
3. Is there any way to save internet bandwidth?
- Minimize connected devices: The more devices using your network (phones, laptops, etc.), the more they compete for bandwidth. Disconnect unused devices.
- Prioritize downloads: Schedule large downloads for off-peak hours when you’re not using the internet heavily.
- Consider streaming quality: Many streaming services offer adjustable video quality settings. Choose lower resolutions to save bandwidth.
4. What is the difference between upload and download bandwidth?
Download bandwidth is receiving data from the internet, like downloading files or streaming videos. Upload bandwidth refers to sending data out to the internet, like uploading photos to social media or video conferencing.
In summary, the above article delved into the crucial roles of bandwidth in electronics, influencing aspects like internet speeds, system capacity, and signal quality. We also discovered formulas to calculate bandwidth for various purposes and factors that can affect it, like cable type and processing power. By understanding bandwidth definition in electronics and the methods to optimize it, you can ensure smoother data flow and a more efficient user experience for your electronic devices.
For an even deeper dive into the intricacies of bandwidth and its impact on the world of electronics, let’s visit Proxy Rotating. There, you’ll find a wealth of information and resources tailored to further enhance your understanding and mastery of this essential topic.
