Blockchain technology stores and transmits information in encrypted, transparent, immutable, and decentralized blocks. In the widespread application context, establishing security standards for blockchain becomes crucial to protect data from cybersecurity threats and enhance transaction credibility. Explore the Proxy Rotating article below to understand the importance of blockchain security standards in strengthening and optimizing blockchain systems and how they shape the technology’s secure future.
Why is blockchain security crucial for information protection?
Blockchain security is crucial for information protection for several key reasons:
Immutable Records
Blockchain technology ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability is essential for protecting the integrity of information, preventing tampering, and ensuring that records remain trustworthy over time.
Decentralization
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes. This decentralization reduces the risk of a single point of failure, making it much harder for attackers to compromise the network. Even if one or several nodes are compromised, the rest of the network functions correctly.
Cryptographic Security
Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. Each block is linked to the previous one through cryptographic hashes, creating a complicated chain to alter without detection. This ensures that the data remains confidential and protected against unauthorized access.
Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain provides a transparent and traceable ledger of all transactions. This transparency allows for the easy auditing of data and the tracking of any changes or transactions. It enhances accountability and reduces the risk of fraudulent activities.
Smart Contracts
Blockchain can utilize smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically enforce rules and obligations, reducing the potential for manual errors and fraud.
Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchain relies on consensus mechanisms (such as Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, etc.) to validate transactions. These mechanisms ensure that all participants agree on the validity of transactions, making it very difficult for malicious actors to alter data without being detected by most of the network.
Resistance to DDoS Attacks
Due to its distributed nature, blockchain is more resistant to Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks than centralized systems. The redundancy and distribution of data across many nodes ensure that the network remains operational even under attack.
User Control and Privacy
Blockchain allows users to have control over their data through private keys. Only the appropriate keys can access and manage the data, providing strong privacy and security. This control is essential for protecting sensitive information.
Reducing Fraud and Counterfeiting
Blockchain’s transparency and immutability make it an effective tool for reducing fraud and counterfeiting. By providing a clear, unchangeable record of transactions, fraudulent activities can be much harder to spot.
Blockchain security is critical for protecting information because it offers a robust, decentralized, and cryptographically secured framework that ensures data integrity, transparency, and privacy. These features make it highly effective in safeguarding information against unauthorized access, tampering, and cyber threats.
Blockchain security standards
Ensuring the blockchain security standards involves adhering to various international and specific security standards designed to safeguard information systems. Among these, essential standards include:
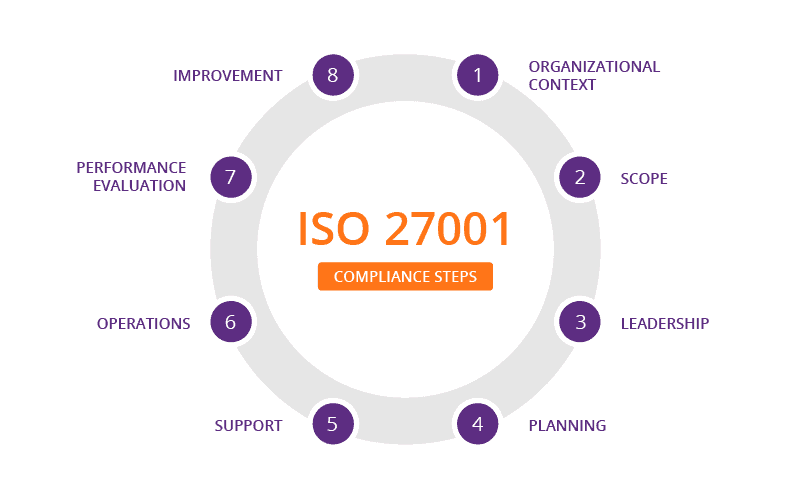
ISO/IEC 27001 standard
Purpose and scope: ISO/IEC 27001 is designed to help organizations establish and maintain an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS). This standard applies to any organization, regardless of size, type, or nature, that aims to protect its information assets securely.
Core elements: It emphasizes the importance of assessing and treating information security risks tailored to the organization’s needs. The standard covers a comprehensive set of controls, categorized into areas such as risk management, security policy, asset management, human resources security, physical and environmental security, communications and operations management, access control, information systems acquisition, development and maintenance, information security incident management, business continuity management, and regulatory compliance.
Impact on Blockchain: For blockchain applications, ISO/IEC 27001 can ensure that the underlying infrastructure and the organizational processes surrounding blockchain deployments adhere to rigorous security practices, safeguarding data integrity, availability, and confidentiality.
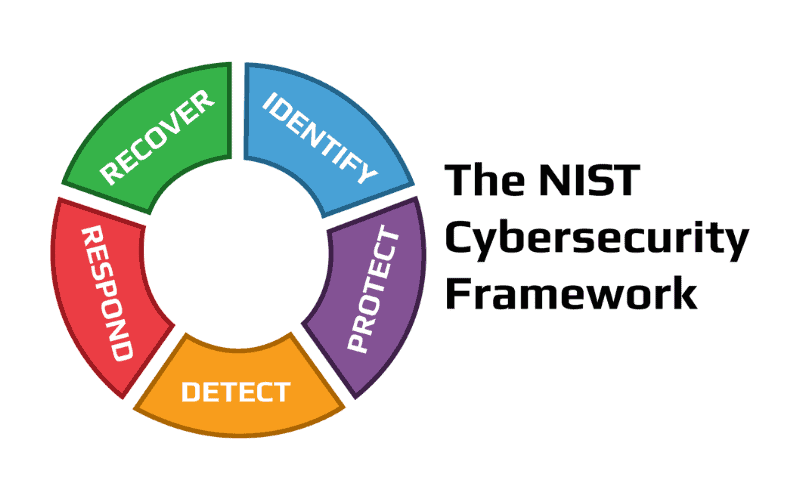
NIST Cybersecurity Framework:
Purpose and Scope: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a policy framework of computer security guidance for how private sector organizations in the US can assess and improve their ability to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber-attacks. It’s flexible enough to be implemented across various sectors and industries.
Core Elements: The framework comprises five main functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. These functions offer a high-level, strategic view of an organization’s cybersecurity risk management lifecycle.
Impact on Blockchain: Applying the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to blockchain technologies helps organizations identify and mitigate risks associated with the deployment and operation of blockchain systems. It ensures the resilience of blockchain applications against cyber threats through continuous identification, protection, detection, response, and recovery practices.
Criterion for Cryptocurrency Security
Purpose and Scope: Specifically tailored for the cryptocurrency ecosystem, the CCSS aims to enhance the security of cryptocurrency systems. It targets entities handling and storing digital currencies, like wallets and exchanges.
Core Elements: The standard outlines critical security requirements for key management, transaction processing, wallet creation, and storage. It focuses on protecting against unauthorized access to funds, ensuring the integrity of transactions, and safeguarding private keys in the custody of service providers.
Impact on Blockchain: By adhering to the CCSS, cryptocurrency businesses can bolster their defenses against common security threats, such as hacking attempts, fraudulent transactions, and asset loss. This standard is vital for building trust among users and investors in the cryptocurrency space.
ERC-721 Standard:
Purpose and scope: ERC-721 introduces a standard for issuing and trading non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on the Ethereum blockchain. It allows for the representation of unique digital assets and collectibles.
Core elements: This standard defines a minimum interface an intelligent contract must implement to allow unique tokens to be managed, owned, and traded. It includes methods for tracking the owner of a unique identifier, transferring tokens, and a way for others to access data about the token.
Impact on Blockchain: ERC-721 has played a crucial role in the explosion of the NFT market by providing a secure and standardized method for representing ownership and transaction of unique digital items. It ensures that NFTs are interoperable across various platforms and marketplaces, enabling a more unified and accessible ecosystem.
Each of these standards addresses specific security aspects within the broader blockchain and digital asset ecosystems, from organizational information security management practices to exact standards for cryptocurrencies and unique digital assets. Their implementation enhances security and fosters trust among users, investors, and regulatory bodies.

Comparing blockchain security standards
When comparing blockchain security standards, it’s essential to understand their distinct purposes, target audiences, and applications within the blockchain ecosystem. Let’s note the key differences and similarities among ISO/IEC 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Cryptocurrency Security Standard (CSS), and ERC-721 Standard.
| Characteristics | ISO/IEC 27001 | NIST Cybersecurity Framework | Cryptocurrency Security Standard (CSS) | ERC-721 Standard |
| Scope and target audience | ISO/IEC 27001 is a broad information security standard applicable across all types of organizations, not exclusively tailored to blockchain technology. It’s designed to help any organization protect its information assets comprehensively. | NIST Cybersecurity Framework offers a set of guidelines aimed at improving cybersecurity across all sectors. Its flexible approach can be adapted to blockchain technologies, among other IT systems. | CSS is designed explicitly for entities dealing with cryptocurrencies. It focuses on securing digital currencies, wallets, and exchanges. It targets a niche within the blockchain sphere, aiming at cryptocurrency service providers. | ERC-721 is a technical standard for the Ethereum blockchain, specifically for creating and managing non-fungible tokens (NFTs). It’s targeted at developers and platforms within the Ethereum ecosystem. |
| Key objectives | ISO/IEC 27001 aims to establish, implement, maintain, and continuously improve an Information Security Management System (ISMS) that ensures information confidentiality, integrity, and availability. | NIST Cybersecurity Framework focuses on identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity threats, offering a comprehensive approach to risk management. | CSS concentrates on the secure management, storage, and transaction of cryptocurrencies, addressing unique challenges in the digital currency space, such as wallet security, transaction integrity, and private key management. | ERC-721 provides a framework for creating, issuing, and trading NFTs, ensuring these digital assets are unique, transferable, and interoperable. |
| Application and Implementation | ISO/IEC 27001 and NIST Cybersecurity Framework can be applied broadly across various blockchain applications, offering foundational security practices that benefit blockchain systems among other IT infrastructures. | CSS and ERC-721, on the other hand, are particular to certain aspects of blockchain technology. CSS applies to cryptocurrency handling, focusing on operational security, while ERC-721 is tailored for NFT markets on the Ethereum platform, focusing on the standardization of unique digital assets. | ||
| Complementarity and Overlap | ISO/IEC 27001 and NIST Cybersecurity Framework provide overarching security management practices that can complement any blockchain technology application. | CSS and ERC-721 address specific needs within the blockchain domain. | ||
While ISO/IEC 27001 and NIST Cybersecurity Framework offer broad, foundational security guidelines applicable across industries and technologies, CSS and ERC-721 provide specialized standards for particular niches within the blockchain ecosystem. Combining these standards can help organizations achieve a comprehensive security posture, addressing general and blockchain-specific security considerations.
Choosing the appropriate blockchain security standards
Choosing the proper blockchain security standards involves assessing the project’s needs, risks, and operational context. Here’s a guide to help you select the most appropriate standards based on different criteria:
Learn about your blockchain application
General vs. Specific Applications: If your blockchain application focuses on data integrity, information sharing, or decentralized processes across various sectors, consider broad standards like ISO/IEC 27001 and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. These provide comprehensive guidelines for managing information security risks that can be applied to various blockchain projects.
Cryptocurrency or Financial Applications: For projects specifically related to cryptocurrencies, wallets, exchanges, or other financial services, CSS (Cryptocurrency Security Standard) is designed to address the unique security challenges of handling digital currencies.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): If your project involves creating, issuing, or trading NFTs on the Ethereum platform, ERC-721 is essential for ensuring the standardization and security of these unique digital assets.
Assess management and compliance needs.
Regulatory requirements vary by region and industry. Projects operating in highly regulated sectors, such as finance or healthcare, must align with specific standards like ISO/IEC 27001 to comply with global and local regulations. Understanding the legal and regulatory landscape is crucial in selecting standards that will help meet compliance obligations.
Consider your safety goals.
Data Integrity and Confidentiality: If the primary objective is to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data, ISO/IEC 27001 provides a robust framework for establishing an ISMS that protects data across its lifecycle.
Risk Management and Cybersecurity: For projects prioritizing comprehensive risk management and cybersecurity, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework offers a flexible and practical approach to identifying, protecting against, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cyber threats.
Secure Transactions and Asset Management: CSS is vital for projects that require secure management and storage of cryptocurrencies. It ensures secure transactions and safeguards against unauthorized access.
Evaluate the project’s technical environment.
Platform-Specific Considerations: For blockchain applications built on the Ethereum platform, especially those dealing with NFTs, adhering to standards like ERC-721 ensures compatibility and security within the Ethereum ecosystem. It’s essential to consider the technical specifics of your blockchain platform when selecting standards.
Look into interoperability and industry best practices
Consider standards that promote interoperability and alignment with industry best practices. ISO/IEC 27001 and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework are widely recognized and can facilitate partnerships and integrations. CSS and ERC-721 ensure alignment with sector-specific best practices for niche areas like cryptocurrencies and NFTs.
Final considerations
Balancing compliance, security objectives, and operational needs is essential when selecting security standards for blockchain projects. Implementing broad security frameworks like ISO/IEC 27001 and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a foundation for managing information security risks. At the same time, adopting standards like CSS and ERC-721 addresses the specific challenges and requirements of cryptocurrency operations and NFT transactions. A thoughtful approach to choosing security standards will not only enhance the security posture of blockchain projects but also contribute to their success and sustainability in the long term.
Implementing security standards for blockchain
Implementing security standards in blockchain projects is crucial for enhancing data integrity, confidentiality, and overall system security. Here’s a structured approach to implementing these standards effectively:
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment
Begin with a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential security threats and vulnerabilities within your blockchain project. This assessment should consider both the technology stack and the operational environment.
- Choose relevant security standards
Based on the risk assessment, select the security standards that align with your project’s needs. ISO/IEC 27001 provides a broad framework for general information security management. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is ideal for comprehensive cybersecurity risk management.
For projects focused on cryptocurrencies or related technologies, consider the Cryptocurrency Security Standard (CSS) for specific guidelines. If dealing with NFTs on the Ethereum platform, ensure ERC-721 compliance for secure and standardized operations.
- Continuous policy and security development
Create a detailed security policy incorporating the selected standards’ requirements and guidelines. This policy should outline security protocols, responsibilities, and procedures for regular operations and incident response.
- Implement security controls and measures
Deploy technical and organizational security controls as specified by the chosen standards. This may include encryption methods, access controls, secure critical management practices, and regular security audits. For ERC-721 compliance, ensure smart contracts for NFTs adhere to the standard’s specifications.
- Educate and train staff
Conduct training sessions for all team members involved in the blockchain project. Ensure they understand the security standards, the importance of compliance, and their roles in maintaining security.
- Regular auditing and compliance checks
Regularly audit your blockchain system and operations against the selected security standards. This includes periodic reviews of security policies, procedures, and technical controls to ensure ongoing compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous monitoring and improvement
Implement continuous real-time monitoring mechanisms to detect and respond to security threats. Use insights from monitoring and auditing to refine security measures and adapt to new threats.
- Engage with security experts
Consider consulting with cybersecurity and blockchain security experts, especially when implementing complex standards like ISO/IEC 27001 or adapting the NIST framework to a blockchain environment. Experts can provide valuable insights into effective implementation and compliance strategies.
- Documentation and record-keeping
Maintain comprehensive documentation of all security policies, procedures, and audit records. This documentation is essential for complying with security standards and facilitating internal reviews and external audits.
- Foster a culture of security
Encourage a security-first culture within your organization. Promote awareness and best practices among all participants, from developers to end-users, to ensure security standards’ effective implementation and upkeep.
Implementing security standards in blockchain projects is a dynamic process that requires ongoing attention and adaptation to technological advancements and evolving security threats. By following these steps and maintaining a proactive stance on security, blockchain projects can achieve high security, integrity, and trust, which are critical for widespread adoption and success.
The impact of security standards on blockchain
Implementing security standards within the blockchain ecosystem profoundly impacts blockchain applications’ security, trustworthiness, and viability. Here’s an overview of the critical impacts:
Improve and enhance data security and integrity
Security standards bring stringent guidelines for data protection, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data stored on blockchain systems. By adopting standards like ISO/IEC 27001 and incorporating specific protocols like the Cryptocurrency Security Standard (CSS) for digital currencies, blockchain networks can protect against unauthorized access and tampering, ensuring that data remains secure and unaltered.
Increase trust and reputation.
Implementing recognized security standards can significantly enhance the trust stakeholders place in a blockchain system. For enterprises and users alike, adherence to standards such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework demonstrates a commitment to cybersecurity, increasing confidence in the system’s ability to protect sensitive information and financial assets.
Regulatory compliance
With the regulatory landscape around blockchain and digital assets evolving, adherence to established security standards helps blockchain projects navigate legal requirements and compliance issues. This is particularly relevant in highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare, where data security and privacy are paramount.
Improved risk management
Security standards provide a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with blockchain technology. Frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework enable organizations to proactively manage cybersecurity risks, reducing the likelihood and impact of security breaches.
Facilitate interoperability
Standards like ERC-721 for non-fungible tokens (NFTs) ensure interoperability among blockchain systems and applications. By defining clear protocols and specifications, these standards enable different blockchain networks and applications to interact seamlessly, fostering a more integrated and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
Attraction of investment
Projects that adhere to established security standards are often viewed as more secure and reliable, attracting investment from individuals and institutions looking to minimize risk. This is especially true for startups and projects in the early stages of development, where establishing trust is critical.
Innovation and development
Security standards also drive innovation within the blockchain space by setting benchmarks for performance and security. As projects strive to meet these standards, they often develop new technologies and methodologies that push the boundaries of what blockchain can achieve, leading to a more dynamic and innovative ecosystem.
Market expansion and adoption
The widespread adoption of security standards contributes to the maturation of the blockchain industry, making it more accessible and appealing to a broader audience. By addressing security concerns and demonstrating reliability, blockchain technology can penetrate new markets and applications, from mainstream financial services to supply chain management.
In conclusion, the impact of blockchain security standards is multifaceted, touching on aspects of security, trust, regulatory compliance, and innovation. As the blockchain industry continues to evolve, the role of these standards will be pivotal in shaping its future, ensuring that blockchain technology can realize its full potential securely and sustainably.
Security standards play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of blockchain systems. Applying suitable standards enhances security capabilities, boosts trust, and drives blockchain development. For more valuable insights into blockchain, cybersecurity, and related content, visit https://proxyrotating.com to explore further.
>>> See more:
Blockchain security in cloud computing
Blockchain security statistics
