Data privacy fundamentals encompass essential practices that safeguard personal data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. Upholding individuals’ privacy rights involves collecting, storing, and utilizing personal data responsibly. This Proxy Rotating article delves into the intricacies of these fundamental principles to provide a deeper understanding of effective data security measures.
What is Data Privacy, and Why is it Important?
Data privacy protects personal or sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. It encompasses individuals’ rights to control how organizations collect, process, and share their data.
Data privacy is essential for several reasons:
- Protection of Personal Information: Data privacy ensures that individuals’ personal information, such as their name, address, email, phone number, financial details, and medical records, is kept confidential and secure. This helps prevent identity theft, fraud, and other forms of misuse of personal data.
- Trust and Reputation: Maintaining data privacy fosters trust between individuals and organizations. When individuals trust that their data is handled responsibly and by privacy regulations, they are likelier to engage with businesses and share their information. Conversely, data breaches or privacy violations can damage an organization’s reputation and erode customer trust.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Data privacy laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, require organizations to protect individuals’ privacy rights and implement appropriate safeguards for handling personal data. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in hefty fines and legal consequences for organizations.
- Ethical Considerations: Respecting individuals’ privacy rights is a moral imperative. Organizations are responsible for collecting and processing personal data only for legitimate purposes and with individuals’ consent. Upholding data privacy principles demonstrates respect for individuals’ autonomy and dignity.
- Data Security: Data privacy and data security are closely linked. Protecting data privacy involves implementing robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber-attacks. By safeguarding data privacy, organizations also enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
- Personal Freedom and Autonomy: Data privacy empowers individuals to maintain control over their personal information and make informed decisions about how it is used. Organizations promote personal freedom and autonomy by respecting individuals’ privacy preferences and giving them transparency and control over their data.
Data privacy is essential for protecting individuals’ rights, fostering trust, complying with regulations, upholding ethical standards, enhancing cybersecurity, and promoting personal freedom and autonomy in the digital age.

Discover what the Data privacy fundamentals are
Understanding data privacy fundamentals is essential for preserving sensitive information’s confidentiality, integrity, and security. These principles guide organizations in handling data responsibly and ethically.
Data Collection: Organizations should only collect data necessary for specific and legitimate purposes. Transparency with individuals regarding the data collection process is essential to establish trust and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Data Storage: Using appropriate technical and physical safeguards, data must be securely stored. This includes encryption, access controls, regular backups, and secure storage facilities to prevent unauthorized access, modification, or data loss.
Data Usage: Organizations should use collected data only for the purposes stated at the time of collection and with the explicit consent of the individuals involved. Any deviation from the stated purposes should be communicated and agreed upon by the data subjects.
Data Access: Individuals can access, modify, and delete organizations’ data. Providing mechanisms for individuals to exercise these rights ensures transparency and accountability in data processing.
Data Sharing: Organizations should only share data with trustworthy third parties with appropriate security measures to protect the data. Data sharing should be based on legal requirements, contractual agreements, and the principle of data minimization to limit exposure and mitigate risks.

What makes data security crucial?
Data security is of paramount importance due to several critical reasons. Firstly, it protects sensitive information, including personal data, trade secrets, and intellectual property, from unauthorized access or disclosure. This protection is essential for maintaining individuals’ privacy and preserving the integrity of businesses. Secondly, data security measures help prevent data breaches, which can lead to severe financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is another crucial aspect of data security, as it helps organizations avoid fines, penalties, and legal consequences. Moreover, effective data security practices are vital for building and maintaining trust with customers and stakeholders, as they demonstrate a commitment to protecting their privacy and security.
Finally, robust data security measures are essential for preventing identity theft, fraud, and other malicious activities resulting from unauthorized access to sensitive information. Overall, investing in data security is critical for organizations to safeguard their data assets, mitigate risks, and maintain the trust and confidence of stakeholders.

The role of individuals in personal data protection
Understanding privacy rights and taking control of personal data are crucial roles individuals play in protecting their personal information. By being knowledgeable about privacy rights, individuals can effectively advocate for themselves regarding collecting, using, and sharing their data. Moreover, exercising control over personal data entails making informed decisions about sharing personal information and determining how organizations use it.
Additionally, individuals are responsible for reporting any violations of data security practices and helping to prevent and address breaches or unauthorized access to personal data. Overall, individuals’ proactive engagement in safeguarding their personal information is essential for maintaining privacy and data security in an increasingly digital world.

Benefits of adhering to data privacy fundamentals
Adhering to basic principles of data security yields numerous benefits:
- Protection of Personal Privacy Rights: By following data security principles, organizations ensure that individuals’ personal information is handled with care and respect, safeguarding their privacy rights and preventing unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive data.
- Enhanced Customer Trust: Demonstrating a commitment to data security instills confidence in customers, assuring them that their information is safe and secure. This trust strengthens the relationship between organizations and their customers, increasing loyalty and satisfaction.
- Compliance with Legal Requirements: Adhering to data security principles ensures compliance with relevant laws and regulations governing the handling of personal data. By meeting legal obligations, organizations mitigate the risk of facing fines, penalties, or legal consequences for non-compliance.
- Elevation of Brand Reputation: Upholding high data security standards enhances organizations’ reputation and credibility. By prioritizing protecting personal data, organizations signal their integrity, reliability, and commitment to ethical business practices, improving their brand image and attracting more customers.
How to Enhance Data Privacy in Your Organization?
Enhancing data privacy in an organization is crucial for protecting sensitive information, maintaining trust, and complying with regulations. Here are key strategies:
Develop a Comprehensive Data Privacy Policy
- Policy Framework: Establish a clear policy outlining data handling practices.
- Compliance: Ensure alignment with relevant data protection laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
Conduct Regular Data Audits
- Inventory: Track data assets, including storage and access details.
- Data Flow Mapping: Identify potential vulnerabilities.
Implement Data Minimization Principles
- Necessity: Collect only essential data.
- Retention Policies: Define and enforce data retention and secure deletion policies.
Use Strong Encryption
- At Rest and In Transit: Encrypt data in both states.
- Key Management: Implement robust critical management practices.
Strengthen Access Controls
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign access based on roles.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for sensitive data access.
Regular Security Training and Awareness Programs
- Employee Training: Regularly educate employees on data privacy and phishing threats.
- Simulated Attacks: Conduct phishing and cyber-attack exercises.
Implement Robust Incident Response Plans
- Preparation: Develop and update response plans for data breaches.
- Testing: Regularly test these plans.
Deploy Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
- Monitoring: Use DLP tools to track and control data movement.
- Prevention: Block unauthorized data transfers.
Ensure Vendor and Third-Party Compliance
- Due Diligence: Verify third-party compliance with your privacy standards.
- Contracts: Include privacy requirements in third-party agreements.
Regularly Update Software and Systems
- Patching: Keep software and systems up to date with security patches.
- Vulnerability Management: Conduct regular vulnerability assessments.
Employ Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
- Anonymization: Use anonymization and pseudonymization techniques.
- Differential Privacy: Implement methods to minimize re-identification risks.
Engage with Data Privacy Experts
- Consultation: Seek advice from privacy experts and legal counsel.
- Certifications: Encourage staff to earn data privacy certifications.
Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance an organization’s data privacy posture, safeguarding sensitive information and building stakeholder trust.
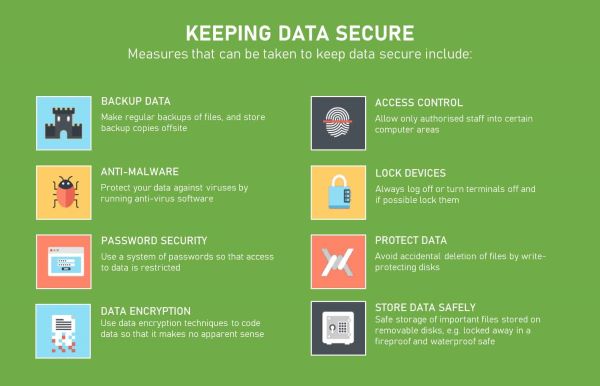
How can you safeguard your personal information?
Protecting your data is essential in today’s digital age, underscoring the importance of understanding data privacy fundamentals. Start by being mindful of what information you share online and only provide necessary details on trusted websites and platforms. Use strong, unique passwords for each online account and enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible to add an extra layer of security. Regularly update your software and devices to patch any vulnerabilities hackers could exploit.
Exercise caution with unexpected emails or messages, and refrain from clicking on dubious links or downloading files from unfamiliar sources. Consider using encryption tools and secure messaging apps to communicate sensitive information, aligning with data privacy fundamentals to safeguard your communications. Finally, regularly review your privacy settings on social media platforms and other online services to control who can access your data. By adopting these practices, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized access to your personal information and protect yourself from identity theft, fraud, and other cyber threats.
Understanding the data privacy fundamentals is crucial in safeguarding personal information in an increasingly digital world. Individuals and organizations can protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, and disclosure by adhering to data minimization, purpose limitation, and user consent. Additionally, empowering individuals with control over their data and ensuring compliance with data protection laws are essential to enhancing privacy and maintaining trust. For further insights and guidance on data privacy fundamentals, visit proxyrotating.com.
>> See more:
Data privacy vs confidentiality
